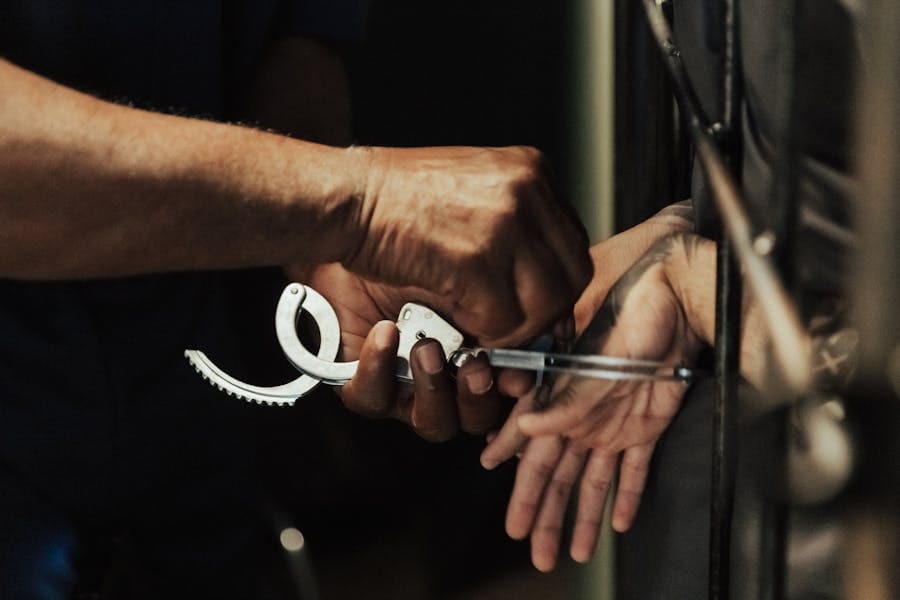
This is a common question faced by many individuals who encounter legal issues related to violent offenses. Assault is a criminal charge that can be classified as either a misdemeanor or a felony, depending on the severity of the incident and the circumstances involved. Generally, an assault becomes a felony when it involves aggravating factors such as the use of a weapon, serious bodily harm, or the intent to cause severe injury.
The distinction between misdemeanor and felony assault is critical because the legal consequences vary significantly. A misdemeanor assault charge may result in fines, probation, or short-term imprisonment, while a felony assault charge can lead to much harsher penalties, including lengthy prison sentences and a permanent criminal record. This guide will delve into the factors that determine whether assault is classified as a felony, the legal implications, and what you should know if you or someone you know faces assault charges.
Is assault a felony?
Assault can be classified as either a misdemeanor or a felony, depending on the severity of the offense. A misdemeanor assault typically involves minor injuries or the threat of harm without serious consequences. However, assault becomes a felony when it involves aggravating factors such as the use of a weapon, severe bodily injury, or the intent to inflict significant harm. Felony assault carries more severe penalties, including longer prison sentences and higher fines. It’s essential to understand the legal definitions and potential consequences to navigate these charges effectively.
Understanding Legal Definitions
Assault can be a confusing term in legal contexts because it varies in definition and classification. In general, assault is defined as an intentional act that causes another person to fear imminent physical harm. However, not all assault charges are considered felonies. The classification depends on the severity of the act and the presence of specific aggravating factors.
In most jurisdictions, assault can be either a misdemeanor or a felony. Misdemeanor assault involves less severe acts, such as minor threats or physical contact that does not result in significant injury. On the other hand, felony assault is more serious and includes incidents where the victim suffers severe injuries or the perpetrator uses a deadly weapon. Felony assault is treated as a violent crime, leading to harsher penalties, including long-term imprisonment and permanent criminal records.
Understanding the differences between misdemeanor and felony assault is crucial for anyone facing these charges. The legal system considers the intent behind the act, the extent of harm caused, and the use of weapons in determining the severity of the charge.
When Is Assault Considered a Felony? Key Factors to Consider
Aggravating Circumstances
In legal terms, assault is classified as a felony when there are aggravating circumstances. This includes the use of a deadly weapon, such as a gun or knife, which significantly elevates the severity of the offense. Even the mere threat of using a weapon can result in a felony charge if the victim believes their life is in danger.
Intent to Cause Severe Harm
Felony assault often involves the intent to cause severe bodily injury. If the perpetrator acted to inflict serious harm, the charge is likely to be elevated from a misdemeanor to a felony.
Extent of the Victim’s Injuries
The severity of the victim’s injuries plays a crucial role in determining the charge. Minor injuries may lead to misdemeanor charges, while severe injuries, such as broken bones, disfigurement, or long-term disabilities, can result in felony assault charges.
Assault on a Protected Individual
Assaulting certain individuals, such as police officers, teachers, or healthcare workers, is automatically classified as a felony. The law recognizes these professions as protected due to the nature of their work and the risks they face.
Types of Felony Assault Charges
Felony assault is a serious offense that can take several forms, each with specific legal definitions and varying levels of penalties. Understanding the different types of felony assault charges is essential, as the classification often influences the severity of the consequences. Here are some common types of felony assault charges and what they entail.
1. Aggravated Assault
Aggravated assault is considered one of the most severe types of assault charges. It typically involves the use of a deadly weapon or the infliction of severe bodily harm on the victim. A deadly weapon can include firearms, knives, or any object capable of causing life-threatening injuries. Aggravated assault charges often arise from incidents where the victim sustains serious injuries, such as broken bones, disfigurement, or permanent disabilities. The penalties for aggravated assault are harsh, often including long-term imprisonment, heavy fines, and mandatory participation in anger management or rehabilitation programs. This charge is treated as a violent felony and can result in a permanent criminal record.
2. Assault with a Deadly Weapon
Assault with a deadly weapon involves the use or threat of use of any weapon that can cause fatal injuries. This type of charge applies when the perpetrator uses a gun, knife, bat, or similar object during the assault. Even if the weapon was not actually used but merely brandished or threatened, it can still lead to a felony charge. The law takes the potential for severe harm seriously, and as a result, the penalties are significant. A conviction for assault with a deadly weapon may include lengthy prison sentences, substantial fines, and a requirement to register as a violent offender, depending on the jurisdiction.
3. Domestic Assault
Domestic assault refers to assault that occurs within a domestic setting, such as between spouses, intimate partners, family members, or individuals living together. Domestic assault can quickly escalate to a felony charge if it involves serious injuries or the use of a weapon. The law treats domestic assault cases with particular severity due to the ongoing threat to the victim’s safety and well-being. Convictions may result in prison time, restraining orders, loss of child custody, and mandatory participation in domestic violence counseling. Domestic assault charges can also have a lasting impact on the defendant’s personal and professional life, including restrictions on firearm ownership.
Legal Consequences of Felony Assault
The legal consequences of felony assault are severe and can have a lasting impact on an individual’s life:
- Lengthy Prison Sentences:
Felony assault convictions often result in significant prison time, ranging from several years to life imprisonment, depending on the severity of the offense. - Heavy Fines and Restitution:
Offenders may be required to pay substantial fines and provide restitution to the victim for medical expenses and other damages. - Permanent Criminal Record:
A felony conviction results in a permanent criminal record, which can affect future employment, housing, and legal rights, including the right to vote or own firearms. - Mandatory Anger Management Programs:
Courts may require the offender to attend anger management or rehabilitation programs as part of their sentence.
Defending Against Felony Assault Charges
Facing felony assault charges can be daunting, but several legal defenses may be available depending on the circumstances of the case. Understanding these potential defenses is crucial for building a strong legal strategy. Here are some common defenses used to contest felony assault allegations.
Self-Defense
One of the most common defenses against felony assault charges is self-defense. In this argument, the defendant claims that the assault was a necessary response to an immediate threat or danger to their safety. To successfully use this defense, the defendant must prove that they were acting to protect themselves from physical harm and that the force used was reasonable and proportional to the threat they faced. For example, if the defendant was being physically attacked or felt threatened by another individual, they may argue that their actions were justified as a means of self-protection. This defense hinges on the presence of a credible threat and the absence of excessive or unnecessary force.
Consent
Another possible defense is consent, which can be used in cases where the alleged victim agreed to the physical contact. In some situations, the defendant may argue that the contact was consensual, especially if the parties were engaged in a mutually agreed-upon activity, such as contact sports or certain social interactions. However, this defense is limited and may not apply if the consent was coerced or if the victim was unable to legally provide consent, such as in cases involving minors. For the consent defense to hold, it must be proven that both parties willingly engaged in the activity without any force or manipulation.
Lack of Intent
A lack of intent defense focuses on the argument that the defendant did not deliberately intend to cause harm. In felony assault cases, the prosecution must prove that the defendant acted with the intent to inflict serious injury. If the defendant can demonstrate that their actions were accidental or that there was no intent to cause harm, it may reduce the charges or result in an acquittal. For example, if the defendant’s actions were part of an accidental collision or an unintended consequence of a separate incident, they may argue that the injuries were not caused intentionally. This defense is particularly relevant in cases where the physical contact was unplanned or occurred in the heat of the moment.
Conclusion
Assault charges can be classified as either a misdemeanor or a felony. Misdemeanor assault generally involves minor injuries or threats that do not result in significant harm. In contrast, felony assault typically involves more severe factors, such as the use of a deadly weapon, intent to inflict serious injury, or causing severe bodily harm to the victim.
The classification of assault as a felony significantly raises the stakes, as the legal consequences are much more severe. Felony assault can result in lengthy prison sentences, substantial fines, and a permanent criminal record, which can impact various aspects of a person’s life, including employment and legal rights. It is crucial to understand the specific legal definitions and the factors that elevate an assault charge to a felony.
Awareness of potential defenses, such as self-defense or lack of intent, can be vital for anyone facing such charges. Knowing these distinctions helps individuals better navigate the complexities of assault cases and make informed decisions about their legal options.
FAQ’s
Q. Is assault always considered a felony?
A. No, assault can be classified as either a misdemeanor or a felony, depending on the severity of the act and the circumstances involved.
Q. What factors make assault a felony?
A. Factors like the use of a deadly weapon, severe injuries, and assault on a protected individual typically elevate the charge to a felony.
Q. Can you go to jail for misdemeanor assault?
A. Yes, misdemeanor assault can result in jail time, but the sentences are usually shorter than for felony assault.
Q. What is aggravated assault?
A. Aggravated assault involves serious bodily injury or the use of a deadly weapon and is always classified as a felony.
Q. Can self-defense be a valid defense against assault charges?
A. Yes, self-defense is a common legal defense against assault charges, provided the defendant can prove they acted to protect themselves from harm.